
|
|
PDF HIP6019 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | HIP6019 | |
| Descripción | Advanced Dual PWM and Dual Linear Power Control | |
| Fabricantes | Intersil Corporation | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de HIP6019 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 15 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
Data Sheet
HIP6019
April 1998 File Number 4490.2
Advanced Dual PWM and Dual Linear
Power Control
The HIP6019 provides the power control and protection for four
output voltages in high-performance microprocessor and
computer applications. The IC integrates two PWM controllers,
a linear regulator and a linear controller as well as the
monitoring and protection functions into a single 28 lead SOIC
package. One PWM controller regulates the microprocessor
core voltage with a synchronous-rectified buck converter, while
the second PWM controller supplies the computer’s 3.3V power
with a standard buck converter. The linear controller regulates
power for the GTL bus and the linear regulator provides power
for the clock driver circuits.
The HIP6019 includes an Intel-compatible, TTL 5-input digital-
to-analog converter (DAC) that adjusts the core PWM output
voltage from 2.1VDC to 3.5VDC in 0.1V increments and from
1.8VDC to 2.05VDC in 0.05V steps. The precision reference
and voltage-mode control provide ±1% static regulation. The
second PWM controller is user-adjustable for output levels
between 3.0V and 3.5V with ±2% accuracy. The adjustable
linear regulator uses an internal pass device to provide 2.5V
±2.5%. The adjustable linear controller drives an external N-
Channel MOSFET to provide 1.5V ±2.5%.
The HIP6019 monitors all the output voltages. A single Power
Good signal is issued when the core is within ±10% of the DAC
setting and the other levels are above their under- voltage
levels. Additional built-in over-voltage protection for the core
output uses the lower MOSFET to prevent output voltages
above 115% of the DAC setting. The PWM controller’s over-
current functions monitor the output current by sensing the
voltage drop across the upper MOSFET’s rDS(ON), eliminating
the need for a current sensing resistor.
Pinout
HIP6019 (SOIC)
TOP VIEW
UGATE2 1
PHASE2 2
VID4 3
VID3 4
VID2 5
VID1 6
VID0 7
PGOOD 8
OCSET2 9
FB2 10
COMP2 11
SS 12
FAULT/RT 13
FB4 14
28 VCC
27 UGATE1
26 PHASE1
25 LGATE1
24 PGND
23 OCSET1
22 VSEN1
21 FB1
20 COMP1
19 FB3
18 GATE3
17 GND
16 VOUT4
15 VSEN2
Features
• Provides 4 Regulated Voltages
- Microprocessor Core, I/O, Clock Chip and GTL Bus
• Drives N-Channel MOSFETs
• Operates from +5V and +12V Inputs
• Simple Single-Loop Control Designs
- Voltage-Mode PWM Control
• Fast Transient Response
- High-Bandwidth Error Amplifiers
- Full 0% to 100% Duty Ratios
• Excellent Output Voltage Regulation
- Core PWM Output: ±1% Over Temperature
- I/O PWM Output: ±2% Over Temperature
- Other Outputs: ±2.5% Over Temperature
• TTL-Compatible 5-Bit Digital-to-Analog Core Output
Voltage Selection
- Wide Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.8VDC to 3.5VDC
- 0.1V Steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1VDC to 3.5VDC
- 0.05V Steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.8VDC to 2.05VDC
• Power-Good Output Voltage Monitor
• Microprocessor Core Voltage Protection Against Shorted
MOSFET
• Over-Voltage and Over-Current Fault Monitors
- Does Not Require Extra Current Sensing Element,
Uses MOSFET’s rDS(ON)
• Small Converter Size
- Constant Frequency Operation
- 200kHz Free-Running Oscillator; Programmable from
50kHz to 1MHz
Applications
• Full Motherboard Power Regulation for Computers
• Low-Voltage Distributed Power Supplies
Ordering Information
PART NUMBER TEMP. (oC) PACKAGE
HIP6019CB
0 to 70 28 Ld SOIC
HIP6019EVAL1 Evaluation Board
PKG. NO.
M28.3
2-252
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
http://www.intersil.com or 407-727-9207 | Copyright © Intersil Corporation 1999
1 page 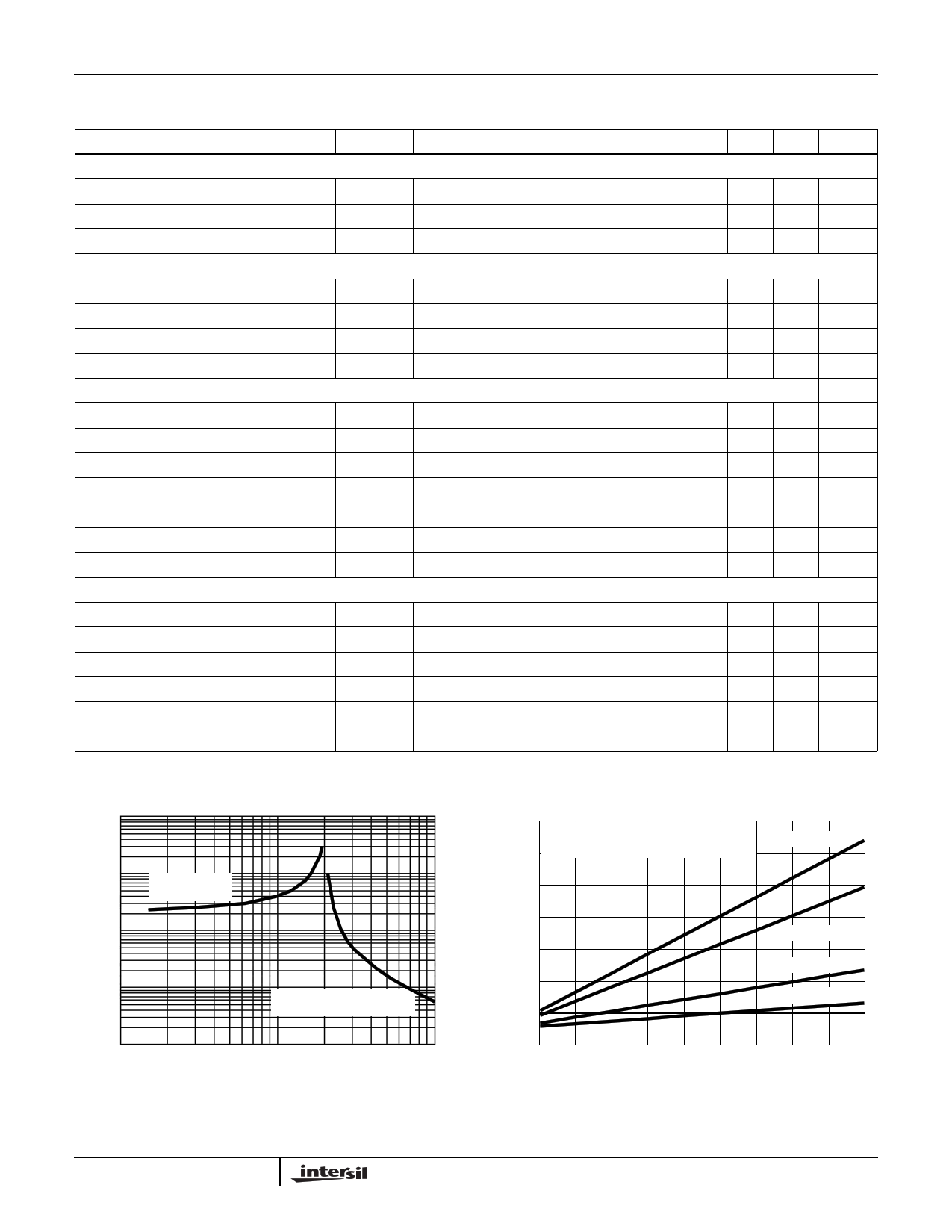
HIP6019
Electrical Specifications Recommended Operating Conditions, Unless Otherwise Noted.
Refer to Figures 1, 2 and 3 (Continued)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST CONDITIONS
PWM CONTROLLER ERROR AMPLIFIERS
DC Gain
Gain-Bandwidth Product
GBWP
Slew Rate
SR COMP = 10pF
PWM CONTROLLER GATE DRIVERS
Drive1 (and 2) Source
Drive1 (and 2) Sink
Lower Gate Source
Lower Gate Sink
PROTECTION
IUGATE
RUGATE
ILGATE
RLGATE
VCC = 12V, VUGATE1 (or VGATE2) = 6V
VGATE-PHASE = 1V
VCC = 12V, VLGATE = 1V
VGATE = 1V
VOUT1 Over-Voltage Trip
VOUT2 Over-Voltage Trip
VSEN2 Input Resistance
VSEN1 Rising
VSEN2 Rising
FAULT Sourcing Current
OCSET1(and 2) Current Source
Soft-Start Current
Chip Shutdown Soft-Start Threshold
IOVP
IOCSET
ISS
VFAULT/RT = 10.0V
VOCSET = 4.5VDC
POWER GOOD
VOUT1 Upper Threshold
VOUT1 Under-Voltage
VOUT1 Hysteresis
VOUT2 Under-Voltage
VOUT2 Under-Voltage Hysteresis
PGOOD Voltage Low
VSEN1 Rising
VSEN1 Rising
Upper/Lower Threshold
VSEN2 Rising
VPGOOD IPGOOD = -4mA
Typical Performance Curves
MIN TYP MAX UNITS
- 88 -
dB
- 15 - MHz
- 6 - V/µs
-1-
- 1.7 3.5
-1-
- 1.4 3.0
A
Ω
A
Ω
112 115 118
4.1 4.3 4.5
- 70 -
10 14
-
170 200 230
- 11 -
- - 1.0
%
V
kΩ
mA
µA
µA
V
108 - 110
92 - 94
-2-
2.45 2.55 2.65
- 100 -
- - 0.5
%
%
%
V
mV
V
1000
100
RT PULLUP
TO +12V
10
RT PULLDOWN TO VSS
140
CUGATE1 = CUGATE2 = CLGATE1 = CGATE
120 VVCC = 12V,VIN = 5V
CGATE = 4800pF
100
80
CGATE = 3600pF
60
CGATE = 1500pF
40
CGATE = 660pF
20
10 100
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (kHz)
FIGURE 4. RT RESISTANCE vs FREQUENCY
1000
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (kHz)
FIGURE 5. BIAS SUPPLY CURRENT vs FREQUENCY
2-256
5 Page 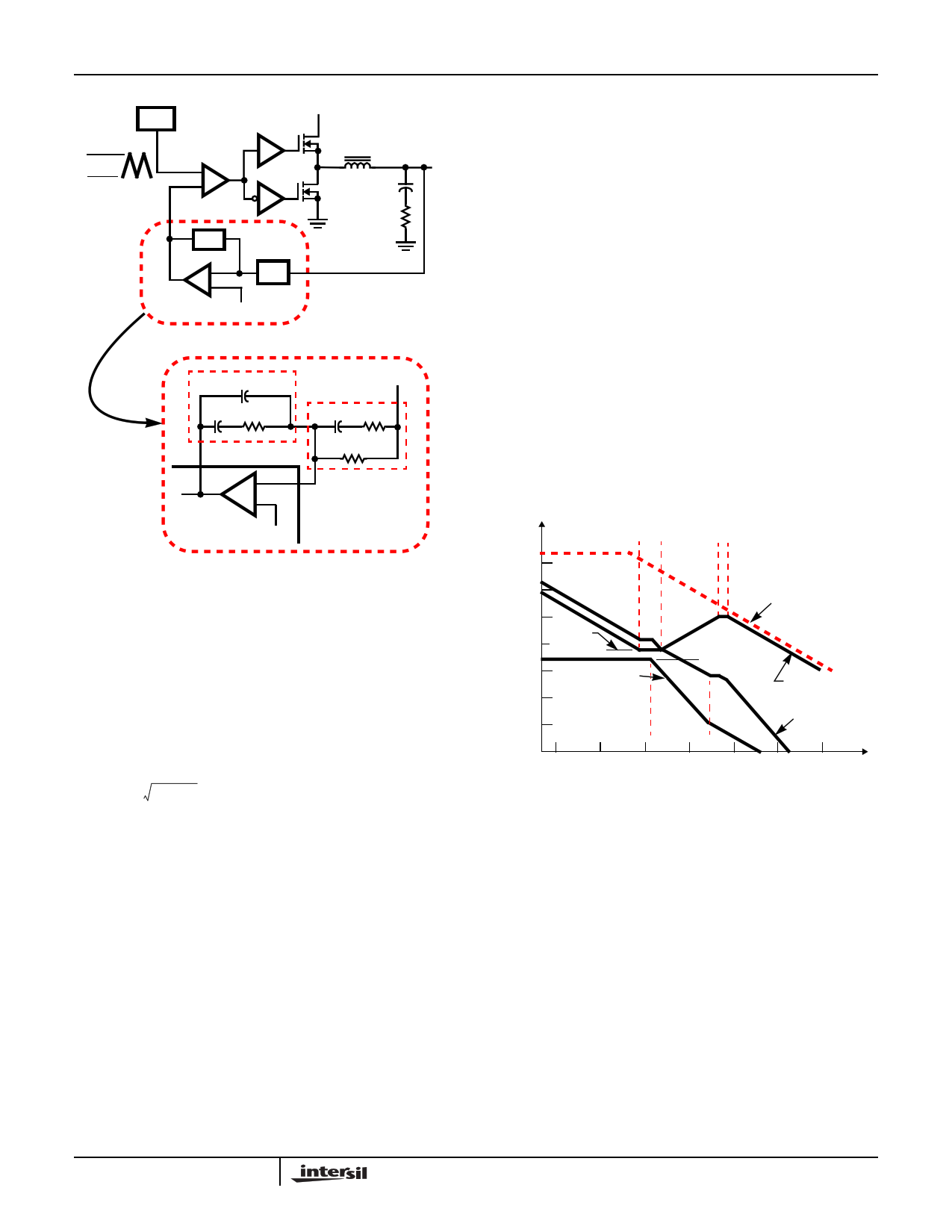
HIP6019
∆VOSC
OSC
PWM
COMP
-
+
DRIVER
DRIVER
ZFB
VE/A
- ZIN
+
ERROR
AMP
REFERENCE
VIN
LO VOUT
PHASE
CO
ESR
(PARASITIC)
DETAILED FEEDBACK COMPENSATION
C2
C1 R2
ZFB VOUT
ZIN
C3 R3
COMP
- FB
+
HIP6019
REFERENCE
R1
FIGURE 11. VOLTAGE-MODE BUCK CONVERTER COMPEN-
SATION DESIGN
The modulator transfer function is the small-signal transfer
function of VOUT/VE/A. This function is dominated by a DC
gain and the output filter, with a double pole break frequency
at FLC and a zero at FESR. The DC gain of the modulator is
simply the input voltage, VIN, divided by the peak-to-peak
oscillator voltage, ∆VOSC.
Modulator Break Frequency Equations
FLC=
-------------------1--------------------
2π × LO × CO
FESR= 2----π-----×-----E----S--1---R------×-----C----O---
The compensation network consists of the error amplifier
internal to the HIP6019 and the impedance networks ZIN
and ZFB. The goal of the compensation network is to
provide a closed loop transfer function with an acceptable
0dB crossing frequency (f0dB) and adequate phase margin.
Phase margin is the difference between the closed loop
phase at f0dB and 180 degrees. The equations below relate
the compensation network’s poles, zeros and gain to the
components (R1, R2, R3, C1, C2, and C3) in Figure 11.
Use these guidelines for locating the poles and zeros of the
compensation network:
1. Pick Gain (R2/R1) for desired converter bandwidth.
2. Place 1ST Zero below filter’s Double Pole (~75% FLC).
3. Place 2ND Zero at filter’s Double Pole.
4. Place 1ST Pole at the ESR Zero.
5. Place 2ND Pole at half the switching frequency.
6. Check Gain against Error Amplifier’s Open-Loop Gain.
7. Estimate Phase Margin - repeat if necessary.
Compensation Break Frequency Equations
FZ1 = 2----π-----×-----R---1--2-----×----C-----1--
FZ2 = 2----π-----×-----(--R-----1-----+-1----R-----3----)---×-----C-----3-
FP1
=
---------------------------1---------------------------
2π
×
R2
×
C-C----11-----+×-----CC-----22--
FP2 = 2----π-----×-----R---1--3-----×----C-----3--
Figure 12 shows an asymptotic plot of the DC-DC
converter’s gain vs frequency. The actual modulator gain has
a peak due to the high Q factor of the output filter at FLC,
which is not shown in Figure 12. Using the above guidelines
should yield a compensation gain similar to the curve
plotted. The open loop error amplifier gain bounds the
compensation gain. Check the compensation gain at FP2
with the capabilities of the error amplifier. The closed loop
gain is constructed on the log-log graph of Figure 12 by
adding the modulator gain (in dB) to the compensation gain
(in dB). This is equivalent to multiplying the modulator
transfer function to the compensation transfer function and
plotting the gain.
100 FZ1 FZ2 FP1 FP2
80
OPEN LOOP
60 ERROR AMP GAIN
40
20LOG
20 (R2/R1)
0 MODULATOR
-20 GAIN
20LOG
(VIN/∆VOSC)
COMPENSATION
GAIN
-40
FLC
FESR
CLOSED LOOP
GAIN
-60
10 100 1K 10K 100K 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
FIGURE 12. ASYMPTOTIC BODE PLOT OF CONVERTER GAIN
The compensation gain uses external impedance networks
ZFB and ZIN to provide a stable, high bandwidth loop. A
stable control loop has a 0dB gain crossing with
-20dB/decade slope and a phase margin greater than 45
degrees. Include worst case component variations when
determining phase margin.
Oscillator Synchronization
The PWM controllers use a triangle wave for comparison with
the error amplifier output to provide a pulse-width modulated
wave. Should the output voltages of the two PWM converters
be programmed close to each other, then cross-talk could
cause nonuniform PHASE pulse-widths and increased output
voltage ripple. The HIP6019 avoids this problem by
synchronizing the two converters 180° out-of-phase for DAC
2-262
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 15 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet HIP6019.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| HIP6011 | Buck Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM) Controller and Output Voltage Monitor | Intersil Corporation |
| HIP6012 | Buck and Synchronous-Rectifier Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM) Controller | Intersil Corporation |
| HIP6013 | Buck Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM) Controller | Intersil Corporation |
| HIP6014 | Buck and Synchronous-Rectifier (PWM) Controller and Output Voltage Monitor | Intersil Corporation |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
