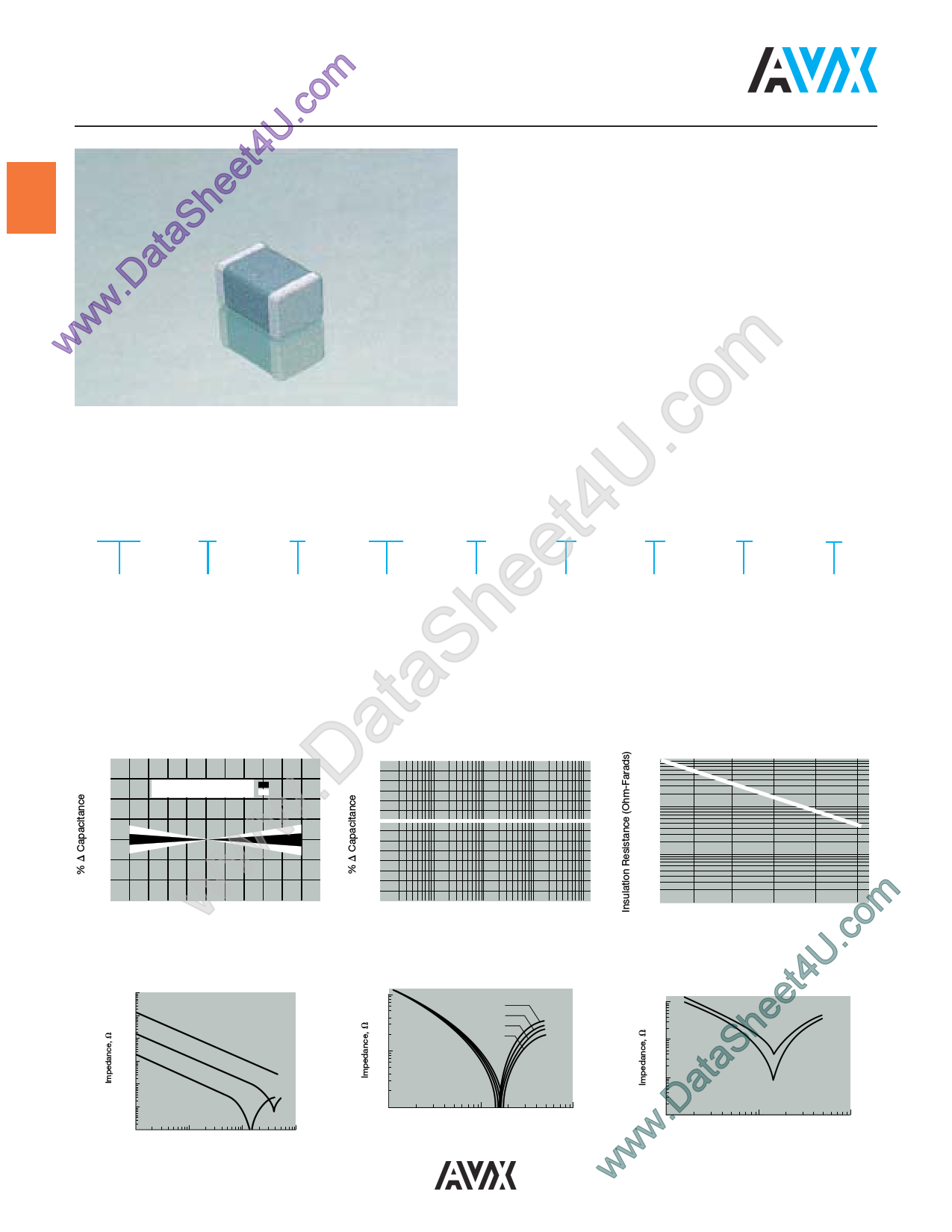
|
|
PDF 18125xxxx Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | 18125xxxx | |
| Descripción | C0G Dielectric | |
| Fabricantes | AVX Corporation | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de 18125xxxx (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 20 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
CGe0neGral(NSpPec0if)ict4DaUtii.oecnolsmectric C0G (NP0) is the most popular formulation of the “tempera-
ture-compensating,” EIA Class I ceramic materials. Modern
e C0G (NP0) formulations contain neodymium, samarium and
he other rare earth oxides.
S C0G (NP0) ceramics offer one of the most stable capacitor
ta dielectrics available. Capacitance change with temperature
a is 0 ±30ppm/°C which is less than ±0.3% ∆ C from -55°C
to +125°C. Capacitance drift or hysteresis for C0G (NP0)
.D ceramics is negligible at less than ±0.05% versus up to
w ±2% for films. Typical capacitance change with life is less
w than ±0.1% for C0G (NP0), one-fifth that shown by most
other dielectrics. C0G (NP0) formulations show no aging
w characteristics.
mThe C0G (NP0) formulation usually has a “Q” in excess
of 1000 and shows little capacitance or “Q” changes with
ofrequency. Their dielectric absorption is typically less than
.c0.6% which is similar to mica and most films.
UPART NUMBER (see page 2 for complete part number explanation)
t40805
5
A 101 J
A
T
2
A
eSize
taShe(L" x W")
Voltage
6.3V = 6
10V = Z
16V = Y
25V = 3
50V = 5
100V = 1
200V = 2
Dielectric
C0G (NP0) = A
Capacitance Capacitance
Failure
Terminations Packaging
Code (In pF) Tolerance
Rate
T = Plated Ni 2 = 7" Reel
2 Sig. Digits + B = ±.10 pF
A = Not
and Sn
4 = 13" Reel
Number of
Zeros
C = ±.25 pF Applicable
D = ±.50 pF
F = ±1% (≥ 25 pF)
G = ±2% (≥ 13 pF)
J = ±5%
K = ±10%
7 = Gold Plated
7 = Bulk Cass.
9 = Bulk
Contact
Factory For
1 = Pd/Ag Term
Contact
Factory
For
Multiples
Special
Code
A = Std.
Product
aTemperature Coefficient
.D+0.5
w0
-0.5
Typical Capacitance Change
Envelope: 0 ± 30 ppm/°C
⌬ Capacitance vs. Frequency
+2
+1
0
-1
-2
Insulation Resistance vs Temperature
10,000
1,000
100
w m-55 -35 -15 +5 +25 +45 +65 +85 +105 +125
w oTemperature °C
.cVariation of Impedance with Cap Value
Impedance vs. Frequency
U0805 - C0G (NP0)
t410 pF vs. 100 pF vs. 1000 pF
100,000
e10,000
he1,000
S100
ta10.0
10 pF
a1.0
.D0.1
w1
10 100
Frequency, MHz
100 pF
1000 pF
1000
ww4
1KHz
10 KHz
100 KHz
Frequency
1 MHz
10 MHz
Variation of Impedance with Chip Size
Impedance vs. Frequency
1000 pF - C0G (NP0)
10
1206
0805
1812
1210
1.0
0.1
10
100
Frequency, MHz
1000
0
0 20 40 60 80
Temperature °C
100
Variation of Impedance with Ceramic Formulation
Impedance vs. Frequency
1000 pF - C0G (NP0) vs X7R
0805
10.00
X7R
NPO
1.00
0.10
0.01
10
100
Frequency, MHz
1000
1 page 
High Voltage Chips
For 500V to 5000V Applications
High value, low leakage and small size are difficult parameters to obtain
in capacitors for high voltage systems. AVX special high voltage MLC
chips capacitors meet these performance characteristics and are
designed for applications such as snubbers in high frequency power
converters, resonators in SMPS, and high voltage coupling/DC blocking.
These high voltage chip designs exhibit low ESRs at high frequencies.
Larger physical sizes than normally encountered chips are used to
make high voltage chips. These larger sizes require that special pre-
cautions be taken in applying these chips in surface mount assem-
blies. This is due to differences in the coefficient of thermal expansion
(CTE) between the substrate materials and chip capacitors. Apply heat
at less than 4°C per second during the preheat. Maximum preheat
temperature must be within 50°C of the soldering temperature.
The solder temperature should not exceed 230°C. Chips 1808 and
larger to use reflow soldering only.
Capacitors with X7R Dielectrics are not intended for AC line filtering
applications.
Contact plant for recommendations. Capacitors may require protective
surface coating to prevent external arcing.
PART NUMBER (see page 2 for complete information and options)
1808
A
A 271 K
A
1
1A
AVX
Style
1206
1210
1808
1812
1825
2220
2225
3640
Voltage
7 = 500V
C = 600V
A = 1000V
S = 1500V
G = 2000V
W = 2500V
H = 3000V
J = 4000V
K = 5000V
Temperature Capacitance Capacitance
Coefficient
Code
Tolerance
A = C0G (2 significant digits C0G: J = ±5%
C = X7R
+ no. of zeros)
Examples:
K = ±10%
M = ±20%
10 pF = 100 X7R: K = ±10%
100 pF = 101
M = ±20%
1,000 pF = 102
Z = +80%,
22,000 pF = 223
-20%
220,000 pF = 224
1 µF = 105
Failure
Rate
A=Not
Applicable
Termination
1= Pd/Ag
T = Plated Ni
and Solder
W
L
Packaging/Marking
1A = 7" Reel
Unmarked
3A = 13" Reel
Unmarked
9A = Bulk/Unmarked
T
t
DIMENSIONS
millimeters (inches)
SIZE
1206
1210
1808*
1812*
1825*
2220*
2225*
3640*
(L) Length
3.20 ± 0.2
3.20 ± 0.2 4.57 ± 0.25 4.50 ± 0.3
4.50 ± 0.3
5.7 ± 0.4
5.72 ± 0.25 9.14 ± 0.25
(0.126 ± 0.008) (0.126 ± 0.008) (0.180 ± 0.010) (0.177 ± 0.012) (0.177 ± 0.012) (0.224 ± 0.016) (0.225 ± 0.010) (0.360 ± 0.010)
(W) Width
1.60 ± 0.2
2.50 ± 0.2 2.03 ± 0.25 3.20 ± 0.2
6.40 ± 0.3
5.0 ± 0.4
6.35 ± 0.25 10.2 ± 0.25
(0.063 ± 0.008) (0.098 ± 0.008) (0.080 ± 0.010) (0.126 ± 0.008) (0.252 ± 0.012) (0.197 ± 0.016) (0.250 ± 0.010) (0.400 ± 0.010)
(T) Thickness
Max.
1.52
(0.060)
1.70
(0.067)
2.03
(0.080)
2.54
(0.100)
2.54
(0.100)
3.3
(0.130)
2.54
(0.100)
2.54
(0.100)
(t) terminal
min.
max.
0.25 (0.010) 0.25 (0.010) 0.25 (0.010) 0.25 (0.010) 0.25 (0.010)
0.75 (0.030) 0.75 (0.030) 1.02 (0.040) 1.02 (0.040) 1.02 (0.040)
0.25 (0.010)
1.02 (0.040)
0.25 (0.010) 0.76 (0.030)
1.02 (0.040) 1.52 (0.060)
*Reflow Soldering Only
39
5 Page 
Basic Capacitor Formulas
I. Capacitance (farads)
English: C = .224 K A
TD
Metric: C = .0884 K A
TD
II. Energy stored in capacitors (Joules, watt - sec)
E
=
⁄1
2
CV2
III. Linear charge of a capacitor (Amperes)
I = C dV
dt
IV. Total Impedance of a capacitor (ohms)
ͱZ = R2S + (XC - XL )2
V. Capacitive Reactance (ohms)
xc
=
2
1
π fC
VI. Inductive Reactance (ohms)
xL = 2 π fL
VII. Phase Angles:
Ideal Capacitors: Current leads voltage 90°
Ideal Inductors: Current lags voltage 90°
Ideal Resistors: Current in phase with voltage
VIII. Dissipation Factor (%)
D.F.= tan ␦ (loss angle) = E.S.R. = (2 πfC) (E.S.R.)
Xc
IX. Power Factor (%)
fP.F. = Sine ␦ (loss angle) = Cos (phase angle)
P.F. = (when less than 10%) = DF
X. Quality Factor (dimensionless)
Q = Cotan ␦ (loss angle) = 1
D.F.
XI. Equivalent Series Resistance (ohms)
E.S.R. = (D.F.) (Xc) = (D.F.) / (2 π fC)
XII. Power Loss (watts)
Power Loss = (2 π fCV2) (D.F.)
XIII. KVA (Kilowatts)
KVA = 2 π fCV2 x 10 -3
XIV. Temperature Characteristic (ppm/°C)
T.C. = Ct – C25 x 106
C25 (Tt – 25)
XV. Cap Drift (%)
C.D. = C1 – C2 x 100
C1
XVI. Reliability of Ceramic Capacitors
( ) ( )L0 = Vt X
Lt Vo
Tt Y
To
XVII. Capacitors in Series (current the same)
Any Number: 1 = 1 + 1 --- 1
CT C1 C2
CN
Two: CT =
C1 C2
C1 + C2
XVIII. Capacitors in Parallel (voltage the same)
CT = C1 + C2 --- + CN
XIX. Aging Rate
DA.R. = % C/decade of time
XX. Decibels
db = 20 log V1
V2
METRIC PREFIXES SYMBOLS
Pico
Nano
Micro
Milli
Deci
Deca
Kilo
Mega
Giga
Tera
X 10-12
X 10-9
X 10-6
X 10-3
X 10-1
X 10+1
X 10+3
X 10+6
X 10+9
X 10+12
K = Dielectric Constant
A = Area
TD = Dielectric thickness
V = Voltage
t = time
Rs = Series Resistance
f = frequency
L = Inductance
␦ = Loss angle
f = Phase angle
X & Y = exponent effect of voltage and temp.
Lo = Operating life
Lt = Test life
Vt = Test voltage
Vo = Operating voltage
Tt = Test temperature
To = Operating temperature
51
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 20 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet 18125xxxx.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| 18125xxxx | C0G Dielectric | AVX Corporation |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |